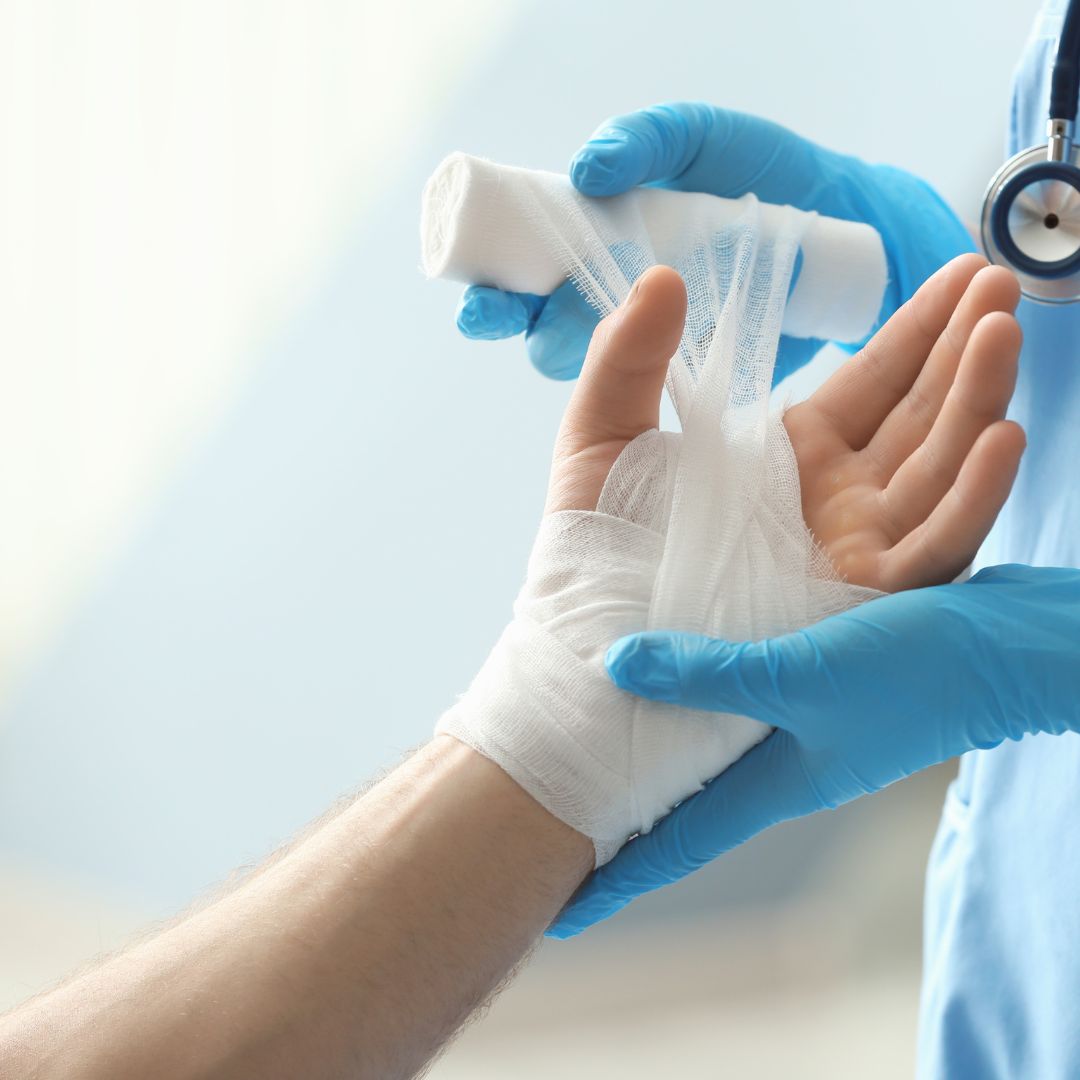
Introduction to medical bandages
Medical bandages play a crucial role in wound care and recovery. Whether you have a minor cut or a more serious injury, selecting the right bandage is essential for optimal healing. In the comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of medical bandages available, their specific uses, and how to choose the appropriate bandage for various injuries or conditions.
The importance of selecting the right medical bandage
Selecting the right medical bandage is vital for promoting proper wound healing and preventing complications. Each type of bandage serves a specific purpose, and understanding their characteristics is essential for effective wound management. Inappropriate bandage selection can lead to delayed healing, infections, and discomfort for the patient.
Understanding the different types
Traditional bandages: gauzes and adhesive bandages
Traditional bandages, such as gauze and adhesive, are commonly used for minor cuts, scrapes, and burns. They are made from woven cotton and provide a sterile environment to promote wound healing. They can be used alone or with antiseptic creams or ointments. Adhesive bandages, on the other hand, are convenient and easy to apply. They have an absorbent pad in the centre and an adhesive strip that sticks to the skin to keep the wound protected.
Elastic bandages: their uses and benefits
Elastic bandages are widely used for providing support, compression, and immobilisation of injured joints, muscles, or ligaments. They are commonly used in sports injuries, sprains, strains and fractures. These are stretchable and provide gentle compression, which helps reduce swelling and promote stability during the healing process. These bandages are available in various widths and lengths to accommodate different body parts.
Compression bandages: for managing swelling and edema
Compression bandages are specifically designed to manage swelling and edema. These apply consistent pressure to the affected area, which helps reduce fluid build-up and improve blood circulation. Compression bandages are often used in the treatment of venous ulcers, cohesive bandages, which stick to themselves without adhesive, or inelastic bandages that require clips or fasteners.
Foam bandages: ideal for wound healing and protection
Foam bandages are highly absorbent and provide a moist wound environment, which promotes healing and protects the wound from external contaminants. These are suitable for moderate to heavily exuding wounds, such as pressure ulcers and surgical wounds. They also provide cushioning and comfort to the wound site, reducing pain and irritation.
Hydrocolloid bandages: promoting moist wound healing
Hydrocolloid bandages are another type of bandage that promotes moist wound healing. They are made of a gel-forming material that absorbs wound exudate and creates a moist environment, which enhances the healing process. Hydrocolloid bandages are commonly used for shallow wounds, blisters, and minor burns. They provide a protective barrier against bacteria and debris while maintaining an optimal moisture balance.
Alginate bandages: for absorbing excess wound exudate
Alginate bandages are highly absorbent and are specifically designed for wounds with excessive exudate. These are made from seaweed-derived fibres and can absorb large amounts of wound fluid. Alginate bandages are commonly used for moderate to heavily exuding wounds, such as venous ulcers and surgical wounds. They form a gel like consistency when in contact with wound exudate, creating a moist environment that promotes healing.
Choosing the right medical bandage for specific injuries or conditions
Choosing the right medical bandages for a specific injury or condition requires careful consideration. Factors such as the type and severity of the wound, the amount of exudate, and the need for compression or immobilisation should be taken into account. Consulting a healthcare professional or wound care specialist can help ensure the appropriate bandage is selected. They can assess the wound and provide guidance on which bandage will best promote healing and prevent complications.
Tips for proper bandage application and removal
Proper application and removal are crucial for the effectiveness of the bandage and the comfort of the patient. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
- Cleanse the wound thoroughly before applying the bandage prevent infection.
- Ensure the bandage is the correct size and shape to adequately cover the wound.
- Apply the bandage snugly but not too tight, allowing for proper circulation and comfort.
- Secure the bandage properly to ensure it stays in place during movement.
- Remove the bandage gently and slowly, following the natural direction of hair growth to minimise pain and skin damage.
The role of medical professionals in bandage selection and application
Medical professionals, such as doctors, nurses, and wound care specialists, play a crucial role in bandage selection and application. They have the knowledge and expertise to assess wounds accurately and determine the most appropriate bandage application techniques and monitor the healing progress. It is essential to consult a medical professional for any significant or complicated wounds to ensure the best possible outcome.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of medical bandages is essential for proper wound care and healing. Each type of bandage serves a specific purpose, and selecting the appropriate one can significantly impact the healing process. Whether it is a traditional gauze bandage, an elastic bandage for support, or a specialised foam or hydrocolloid bandage, choosing the right bandage requires careful consideration of the specific injury or condition. Consultation with medical professionals is crucial to ensure proper selection, application, and overall wound management. By following these guidelines and seeking professional advice when needed, you can confidently navigate the world of medical bandages and promote optimal healing for yourself or your patients.