Burns are one of the most common and painful injuries that occur in every day life. Whether it’s a minor burn from accidentally touching a hot pan or a more severe burn from a fire, it’s important to be aware of burn safety, we will explore the common causes of burns, different types of burns, and provide tips for creating a safe and accident free environment at home, in the workplace, for children and parents, and for environment at home, in the workplace, for children and parents, and for the elderly. Additionally, we will discuss first aid for burns, the importance of burn prevention education, and available resources to prevent burn safety.
The importance of burn safety awareness
Burn safety awareness is crucial in order to prevent burn injuries and create a safe environment. By understanding the risks and taking appropriate measures, individuals can significantly reduce the chances of burns occurring. Burn awareness safety tips are not only essential in public places and workplaces. By incorporating burn safety awareness, we can help prevent accidents and minimise the impact of burn injuries.
Common causes of burns
Burns can be caused by various factors, and being aware of these common causes is the first step in preventing them. The primary causes of burns include:
Heat: Burns from hear sources such as hot liquids, steam, fire, and hot objects are some of the most common types of burns. It is important to exercise caution when working with or being in close proximity to heat sources.
Electricity: Electrical burns can occur when there is contact with live electrical wires or faulty electrical appliances. These burns can range from mild to severe depending on the voltage and duration of exposure.
Chemicals: Chemical burns can result from contact with corrosive substances such as acids, alkalis, or strong cleaning agents. It is crucial to handle chemicals safely, wearing appropriate protective gear and following proper procedures.
Radiation: Burns from radiation exposure based on severity and depth of the injury. Understanding these types can help in assessing the severity of a burn and providing appropriate first aid. The commonly recognised types of burns are:
First degree burns: These burns affect the outer layer of the skin (epidermis) and usually cause redness, pain, and mild swelling. They are considered minor burns and can often be treated at home with first aid measures.
Second degree burns: Second degree burns extend beyond the top layer of the skin and affect the underlying (dermis). They are characterised by redness, blisters, and severe pain. Seeking medical attention is recommended for proper treatment.
Third degree burns: Third degree burns are the most severe and affect all layers of the skin, potentially extending to the underlying tissues. These burns may appear white, brown, or black and can cause significant damage. Immediate medical attention is necessary for third degree burns.
It is important to note that burns can also be classified based on percentage of total body surface area affected. This is particularly important for medical professionals when determining the severity of burns and planning appropriate treatment.
Burn safety tips for the home
Creating a safe environment at home is crucial for preventing burns especially for families with children or elderly individuals. Here’s are some burn safety tips to implement in the home:
- Keep hot liquids and foods out of reach: Ensure the hot beverages and food are placed away from the edges of tables and countertops where children or pets can accidentally knock them over.
- Install and maintain smoke detectors: Smoke detectors are vital for early detection of fires. Install smoke detectors in key areas of the house and regularly check their functionality and battery life.
- Use oven mitts and pot holders: When cooking or baking, always use oven mitts or pot holders, pans, or dishes. Avoid using wet or damp cloths as they can transfer heat more quickly.
- Childproof the kitchen: Install safety gates or locks to restrict access to the kitchen for young children. Keep sharp objects and hot appliances out of reach.
- Set water heater temperature: Adjust the temperature of the water heater to prevent scalding burns. The recommended temperature is below 49 degrees Celsius to reduce the risk of hot water burns.
Implementing these burns safety tips in the home can greatly reduce the risk of burn injuries and create a safer environment for everyone.
Burn safety tips for the workplace
Workplaces can also be prone to burn hazards, depending on the nature of the industry. Employers have a responsibility to ensure a safe working environment and employees should be aware of burn safety tips for the workplace:
Proper handling of equipment: Employees working with hot equipment or materials should be trained on proper handling techniques, including the use of protective gloves, clothing, and equipment.
Fire prevention measures: All workplaces should have adequate fire prevention measures in place, including fire extinguishers, fire alarms, and escape routes. Regular fire drills should be conducted to ensure everyone knows what to do in case of an emergency.
Chemical safety: For workplaces dealing with chemicals, proper storage, handling, and disposal procedures should be followed. Employees should be trained on how to handle chemicals safely and use personal protective equipment (PPE) when necessary.
Electrical safety: Regular inspections of electrical equipment should be carried out to identify and address any potential hazards. Employees should be trained on proper electrical safety protocols including avoiding overloading outlets and using grounded plugs.
By implementing these burn safety tips in the workplace, employers can create a safer environment for their employees and reduce the risk of burn injuries.
Burn safety tips for children and parents
Children are particularly vulnerable to burn injuries due to their natural curiosity and lack of awareness. Parents and caregivers play a crucial role in ensuring the safety of their children. Here are some burn safety tips for children and parents:
Supervision and education: Never leave young children unattended, especially in areas where burn hazards exist. Educate children about the dangers of heat sources and how to handle them safely.
Child resistant packaging: Keep all hazardous substances, such as cleaning agents or medications, out of reach of children. Use child resistant packaging whenever possible to prevent accidental ingestion or exposure.
Water safety: Always supervise children during bath time and ensure the water temperature is safe to prevent scalding burns. Teach children about the dangers of hot water and how to test temperature before getting in.
Fire safety education: Teach children about fire safety, including the importance of not playing with matches or lighters. Practice fire drills at home so that children know what to do in case of a fire emergency.
Parents and caregivers should be proactive in creating a safe environment for children, educating them about burn safety, and closely supervising their activities to prevent burn injuries.
Burn safety tips for the elderly
The elderly population is more susceptible to burns due to factors such as reduced sensitivity to heat, slower reaction times, and medical conditions that can affect mobility. Implementing burn safety measures is crucial for their well being. Here are some burn safety tips for the elderly:
Temperature control: Regularly check the temperature of hot water and adjust the water heater accordingly to prevent scalding burns. Use caution when using heating pads or blankets to avoid over heating.
Proper footwear: Encourage the use of non slip shoes or slippers to prevent falls, which can lead to burns from hot surfaces or cooking equipment.
Kitchen safety: Assist the elderly with cooking tasks to minimise the risks of burns. Ensure the pot handles are turned to prevent accidental spills or contact with hot surfaces.
Home modifications: Make necessary home modifications to create a safer environment for the elderly, such as installing grab bars in bathrooms and removing tripping hazards.
By implementing these burn safety tips, caregivers can help reduce the risk of burn injuries and promote the well being of the elderly.
First aid for burns
Knowing how to administer first aid for burns is crucial in minimising the damage and promoting faster healing. Here are the general steps to follow:
Remove the source of heat: If the burn is caused by a hot object or liquid, remove it from the affected area to prevent further injury.
Cool the burn: Hold the burned area under cool running water for at least 10 minutes to help reduce pain and prevent the burn from worsening. Avoid using ice or very cold water as it can further damage the skin.
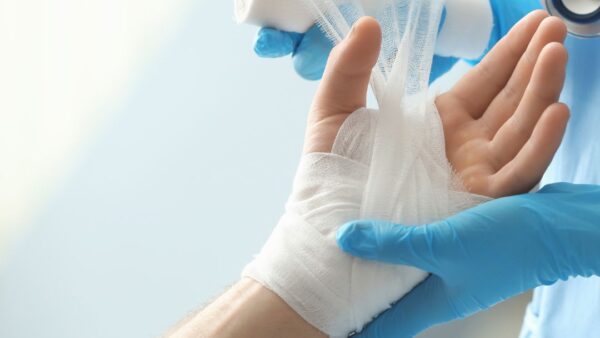
Cover the burn: Use a sterile, non stick dressing or clean cloth to cover the burn and protect it from infection. Avoid using adhesive bandages on the burn.
Seek medical attention: Depending on the severity and size of the burn, it may be necessary to seek medial attention. Third degree burns, burns involving the face, hands, or feet, and burns caused by chemicals or electricity should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Remember these are general first aid steps, and it is important to asses the situation and seek professional medical advice when necessary.
What are best for burns?
Let’s take a look at the BurnSoothe Gel! 🔎
BurnSoothe gel is used to create a barrier between the skin and the environment, helping protect the area from further damage and allowing it to heal. The gel is used to help provide fast relief from the pain and discomfort of a burn, also helping to reduce swelling.
🌱 It includes ingredients such as Aloe Vera and Vitamin E to help soothe the area and reduce the appearance of scars.
Discover our must have Essential First Aid Kit to find all the essential items you need if you find yourself in a situation of needing burn safety equipment.
Creating a safe and accident free environment
In conclusion, burn safety is of utmost importance in maintaining a safe and accident free environment. By being aware of the common causes of burns, understanding the types and severity of burns, and implementing burn safety tips at home, in the workplace, for children and parents, and for the elderly, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of burn injuries. Additionally, knowing how to administer first aid for burns and promoting burn prevention education are crucial aspects of ensuring a safe environment. By following these guidelines and utilising available resources, we can create a society that is well informed and proactive in preventing burn injuries. Remember, burn safety is everyone’s responsibility, and together we can make a difference.